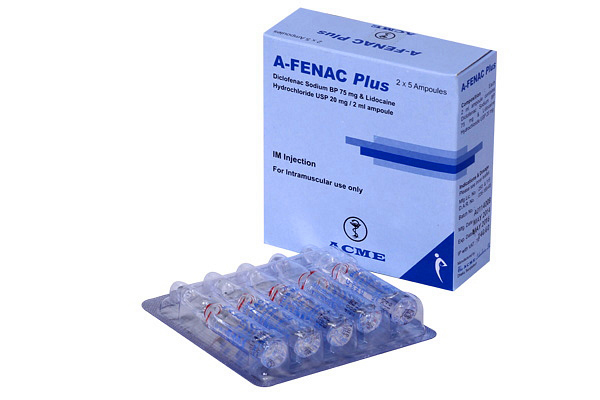
Mobifen Plus Injection (75 mg+20 mg)/2 ml 1 Pcs
Alternative products
Diclofenac Sodium + Lidocaine Hydrochloride
Indications
The injection contains Diclofenac Sodium that is used to relief all grades of pain and inflammation in a wide range of conditions including:
- Arthritic conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, juvenile chronic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, acute gout.
- Acute musculoskeletal disorders such as periarthritis (e.g., Frozen shoulder), tendinitis, tenosynovitis, bursitis.
- Other painful conditions resulting from trauma including, fracture, low back pain, sprains, strains, dislocations, control of pain and inflammation in orthopaedic, dental and other minor surgeries, postoperative pain, pain of renal colic etc.
The injection also contains Lidocaine which acts as a local anaesthetic. Therefore the possibility of pain at the injection site, which is most likely to occur after intramuscular injection, is minimized if the Diclofenac Sodium + Lidocaine Hydrochloride injection is used in the above indications.
Pharmacology
Diclofenac Sodium is a potent nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug (NSAID) with marked analgesic and antipyretic properties. It also has some uricosuric effects. The action of Diclofenac appeared to be associated with the inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. Diclofenac may inhibit synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, an enzyme that catalyses the formation of prostaglandin precursors from arachidonic acid. Peak plasma concentration is achieved within half an hour following injection.
Lidocaine is the most widely used local anaesthetic drug. It acts more rapidly and is more stable than most other local anaesthetics. It is a very useful surface anaesthetic. Like other local anaesthetics, Lidocaine impairs the generation and conduction of nerve impulses by slowing depolarization. The onset of anaesthesia of Lidocaine Hydrochloride is more rapid and the duration is 1-2 hours.
Dosage & Administration
Each 2 ml ampoule contains Diclofenac Sodium 75 mg and Lidocaine Hydrochloride 20 mg.
- Adults: One ampoule once (or in severe cases, twice) daily by intramuscular injection.
- Renal colic: One ampoule once daily intramuscularly. A further ampoule may be administered after 30 minutes, if necessary. The recommended maximum daily dose of diclofenac is 150 mg, by any route. The recommended maximum daily dose of lidocaine is 200 mg.
- Children: In juvenile chronic arthritis, 1-3 mg of diclofenac/kg body wt. daily in divided doses.
- Elderly patients: In elderly or debilitated patients, the lowest effective dosage is recommended, commensurate with age and physical status.
* চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন'
Interaction
Lithium and Digoxin: Diclofenac may increase plasma concentrations of Lithium and Digoxin.
Anticoagulants: There are isolated reports of an increased risk of haemorrhage with the combined use of Diclofenac and anticoagulant therapy, although clinical investigations do not appear to indicate any influence on anticoagulant effect.
Antidiabetic agents: Clinical studies have shown that Diclofenac can be given together with oral antidiabetic agents without influencing their clinical effect.
Cyclosporin: Cases of nephrotoxicity have been reported in patients receiving Cyclosporin and Diclofenac concomitantly.
Methotrexate: Cases of serious toxicity have been reported when Methotrexate and NSAIDs are given within 24 hours of each other.
Quinolone antimicrobials: Convulsions may occur due to an interaction between quinolones and NSAIDs. Therefore, caution should be exercised when considering concomitant therapy of NSAIDs and quinolones.
Other NSAIDs and steroids: Co-administration of Diclofenac with other systemic NSAIDs and steroids may increase the frequency of unwanted effects. With Aspirin, the plasma levels of each are lowered, although no clinical significance is known.
Diuretics: Various NSAIDs are liable to inhibit the activity of diuretics. Concomitant treatment with potassium-sparing diuretics may be associated with increased serum potassium levels. So, serum potassium should be monitored.
Contraindications
It is contraindicated for those patients who are hypersensitive to Diclofenac. In patients with active or suspected peptic ulcer or gastrointestinal bleeding or for those patients in whom attacks of asthma, urticaria or acute rhinitis are precipitated by Aspirin or other NSAIDs possessing prostaglandin synthetase inhibiting activity Diclofenac is also contraindicated. Because of the presence of Lidocaine, this injection is also contraindicated for those patients who are hypersensitive to local anaesthetics of the amide type, although the incidence is very rare. In patients with Adams-Stokes syndrome or with severe degrees of SA, AV, or intraventricular heart block in the absence of an artificial pacemaker, and for those patients who are hypersensitive to any of the excipients used in the formulation (Sodium Metabisulphite, Disodium Edetate, Benzyl Alcohol, Sodium Hydroxide, Propylene Glycol), this injection is also contraindicated.
Side Effects
Side effects to Diclofenac Sodium and Lidocaine injection are usually mild and transient. However if serious side effects occur the injection should be discontinued. Gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, diarrhea and occasionally bleeding may occur. In very rare instances, injection site disorder may occur. In isolated cases, abscesses and local necrosis may occur. The adverse effects due to Lidocaine mainly involve the CNS, are usually of short duration, and are dose related. The CNS reactions may be manifested by drowsiness, dizziness, disorientation, confusion, lightheadedness etc.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Use in Pregnancy: It should not be prescribed during pregnancy, unless there are compelling reasons for doing so. The lowest effective dosage should be used. These types of drugs are not recommended during the last trimester of pregnancy.
Use in Lactation: Very small quantities of Diclofenac may be detected in breast milk, but no undesirable effects on the infant are to be expected.
Precautions & Warnings
Renal: Patients with severe hepatic, cardiac or renal insufficiency or the elderly should be kept under close observation, since the use of NSAIDs may result in deterioration of renal function. The lowest effective dose should be used and renal function should be monitored.
Hepatic: If abnormal liver function tests persist or worsen, clinical signs or symptoms consistent with liver disease develop or if other manifestations occur (eosinophilia, rash), Diclofenac should be discontinued. All patients who are receiving long term treatment with NSAIDs should be monitored as a precautionary measure (e.g., renal, hepatic function and blood counts).
Overdose Effects
Symptoms following acute NSAIDs overdoses are usually limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which are generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding can occur. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression and coma may occur, but are rare. Anaphylactoid reactions have been reported with therapeutic ingestion of NSAIDs, and may occur following an overdose
Therapeutic Class
Drugs for Osteoarthritis, Drugs used for Rheumatoid Arthritis, Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Storage Conditions
Store at temparature not exceeding 30° C in a dry place. Protected from light.
- Type Injection
- Tag
- Morbi leo risus
- Porta ac consectetur ac
- Vestibulum at eros