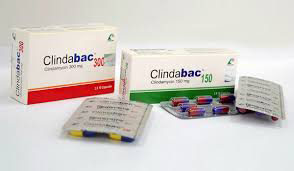
Clindabac Capsule 150 mg 1 Pc
Alternative products
Clindamycin [Oral/Injection]
Composition
- 150 mg capsule: Each capsule contains Clindamycin Hydrochloride BP equivalent to Clindamycin 150 mg.
- 300 mg Capsule: Each capsule contains Clindamycin Hydrochloride BP equivalent to Clindamycin 300 mg.
- Powder for oral solution: Each 5 ml solution contains Clindamycin Palmitate Hydrochloride USP equivalent to Clindamycin 75 mg.
- 300 mg Injection: Each 2 ml Clindacin Sterile Solution contains Clindamycin Phosphate BP equivalent to Clindamycin 300 mg.
- 600 mg Injection: Each 4 ml Clindacin Sterile Solution contains Clindamycin Phosphate BP equivalent to Clindamycin 600 mg.
Indications
Clindamycin has been shown to be effective in the treatment of the following infections when caused by susceptible anaerobic bacteria or susceptible strains of gram positive bacteria such as Streptococci, Staphylococci and Pneumococci; Upper respiratory infections, Lower respiratory infections, Skin and soft tissue infections, Bone and joint infections, Pelvic infections, Intra-abdominal infections, Septicemia and endocarditis, Dental infections. As an alternative therapy when used in combination with quinine or amodiaquine for the treatment of multi-drug resistant Plasmodium falciporum infection.
Description
Clindamycin is a lincosamide antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by susceptible microorganisms. Clindamycin is a semisynthetic antibiotic derived from lincomycin.
Aerobic gram-positive cocci, including: Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis (penicillinase and non-penicillinase producing strains), Streptococci, Pneumococci.
Anaerobic gram-negative bacilli, including: Bacteroides species, Fusobacterium species.
Anaerobic gram-positive non-spore forming bacilli, including: Propionibacterium species, Eubacterium species, Actinomyces species.
Anaerobic and microaerophilic gram-positive cocci, including: Peptococcus species, Peptostreptococcus species, Microaerophilic streptococci, C. perferinges
Dosage & Administration
Dosage of Clindamycin Capsule:
- Serious Infections: 150 mg-300 mg every six hours.
- More severe infections: 300 mg-450 mg every six hours.
To avoid the possibility of oesophageal irritation, Clindacin capsules should be taken with a full glass of water.
Several researches has found that Clindamycin 300 mg capsule provides plasma concentration over MIC90 for more than 12 hours. This finding supports the twice-daily dosing of Clindacin 300 mg capsule, particularly in SSTIs & RTIs. However, in case of bone & joint infections, diabetic foot infections dose of Clindamycin should be 300 mg capsule 3-4 times daily.
Dosage of Clindamycin Powder for oral solution:
- Serious infections: 8-12 mg/kg/day divided into 3 or 4 equal doses.
- Severe infections: 13-16 mg/kg/day divided into 3 or 4 equal doses.
- More severe infections: 17-25 mg/kg/day divided into 3 or 4 equal doses.
In pediatric patients weighing 10 kg or less, 1/2 teaspoon (37.5 mg) three times a day should be considered the minimum recommended dose.
Dosage of Clindamycin IV/IM Injection:
Adults-
- Serious infections due to aerobic gram-positive cocci and the more susceptible anaerobes: 600-1200 mg/day in 2- 4 equal doses.
- More severe infections: 1200-2700 mg/day in 2-4 equal doses.
- For more serious infections: these doses may have to be increased. In life-threatening situations due to either aerobes or anaerobes, these doses may be increased.
- Doses of as much as 4800 mg daily have been given intravenously to adults. Single intramuscular injections of greater than 600 mg are not recommended.
Neonates (less than 1 month): 15 to 20 mg/kg/day in 3 to 4 equal doses. The lower effective dosage may be adequate for small prematures.
Pediatric patients (1 month of age to 16 years):
- 20 to 40 mg/kg/day in 3 or 4 equal doses. The higher doses would be used for more severe infections.
- Parenteral therapy may be changed to Capsules (clindamycin hydrochloride) when the condition warrants and at the discretion of the physician.
- In cases of (3-hemolytic streptococcal infections, treatment should be continued for at least 10 days.
* চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন'
Interaction
Clindamycin enhances the action of other neuromuscular blocking agents. Therefore, it should be used with caution in patients receiving such agents. Antagonism has been demonstrated between clindamycin and erythromycin in vitro. Because of possible clinical significance, these two drugs should not be administered concurrently.
Contraindications
Clindamycin is contraindicated in patients previously found to be sensitive to clindamycin or any of the ingredients of this medicine.
Side Effects
The adverse effects have been reported with the use of clindamycin are- abdominal pain, oesophagitis and oesophagial ulcer, nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea, pruritus, skin rashes, urticaria.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy Category B. Clindamycin crosses the placenta in humans. After multiple doses, amniotic fluid concentrations were approximately 30% of maternal concentrations. Clindamycin should be used in pregnancy only if clearly needed. Clindamycin has been reported to appear in breast milk. Therefore, it is not recommended for nursing mothers if not clearly needed.
Precautions & Warnings
Clindamycin should be prescribed with caution in individuals with a history of gastrointestinal disease, particularly colitis.
Use in Special Populations
Use in newborns and infants: When Clindamycin is administered to newborns and infants (birth to 16 years), appropriate monitoring of organ system functions is desirable.
Geriatric use: Dose adjustment of Clindamycin is not necessary.
Overdose Effects
Overdosage with orally administered clindamycin has been rare. Adverse reactions similar to those seen with normal doses can be expected, however, unexpected reactions could occur. Haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are not effective in removing clindamycin from the serum. Overdosage should be treated with simple gastric lavage. No specific antidote is known.
Therapeutic Class
Macrolides
Reconstitution
Direction for reconstitution (powder for oral solution): Shake the bottle well to loosen the powder. Add 80 ml of boiled and cooled water to the dry mixture in the bottle. For ease of preparation, add water to the bottle in two proportions. Shake well after each addition until all the powder is in solution. Keep the bottle tightly closed. The reconstituted solution should be used within 2 weeks if kept at room temperature.
Dilution of Clindamycin injection for intravenous use: Clindamycin phosphate must be diluted prior to IV administration. The concentration of clindamycin in diluent for infusion should not exceed 18 mg per ml. Infusion rates should not exceed 30 mg per minute.
- Administration of more than 1200 mg in a single 1 hour infusion is not recommended.
- Single IM injections of greater than 600 mg are not recommended. Dilution is not required for intramuscular administration.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Dilution and Compatibility: Physical and biological compatibility studies monitored for 24 hours at room temperature have demonstrated no inactivation or incompatibility with the use of Clindamycin phosphate Sterile Solution (clindamycin phosphate) in IV solutions containing sodium chloride, glucose, calcium or potassium, and solutions containing vitamin B complex in concentrations usually used clinically. No incompatibility has been demonstrated with the antibiotics cephalothin, kanamycin, gentamicin, penicillin or carbenicillin.
Physico-Chemical Stability of diluted solutions of Clindacin Injection-
- Room temperature: 16 days at 25°C.
- Refrigeration: 32 days at 4°C.
Storage Conditions
Keep below 30°C temperature, away from light & moisture. Keep out of the reach of children.
- Type Capsule
- Tag
- Morbi leo risus
- Porta ac consectetur ac
- Vestibulum at eros